427 lines
12 KiB
Plaintext
427 lines
12 KiB
Plaintext
{
|
||
"cells": [
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"%matplotlib inline"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"Neural Networks\n",
|
||
"===============\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"使用torch.nn包来构建神经网络.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"上一讲已经讲过了``autograd`` ,``nn``包依赖``autograd``包来定义模型并求导.\n",
|
||
"一个n``nn.Module``包含各个层和一个``forward(input)``方法,该方法返回``output``.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"例如\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"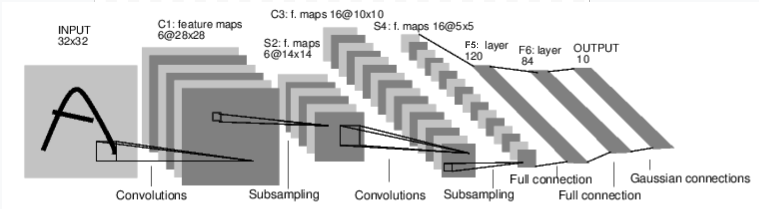\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"他是一个简单的前馈神经网络,它接受一个输入,然后一层接着一层的的传递,最后输出计算的结果.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"神经网络的典型训练过程如下:\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"1. 定义包含一些可学习的参数(或者叫权重)神经网络模型 \n",
|
||
"2. 在数据集上迭代; \n",
|
||
"3. 通过神经网络处理输入; \n",
|
||
"4. 计算损失(输出结果和正确值的差值大小) \n",
|
||
"5. 将梯度反向传播会网络的参数; \n",
|
||
"6. 更新网络的参数,主要使用如下简单的更新原则: \n",
|
||
"``weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient``\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" \n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"定义网络\n",
|
||
"------------------\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"开始定义一个网络:\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [
|
||
{
|
||
"name": "stdout",
|
||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||
"text": [
|
||
"Net(\n",
|
||
" (conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))\n",
|
||
" (conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))\n",
|
||
" (fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)\n",
|
||
" (fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)\n",
|
||
" (fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)\n",
|
||
")\n"
|
||
]
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"import torch\n",
|
||
"import torch.nn as nn\n",
|
||
"import torch.nn.functional as F\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"class Net(nn.Module):\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" def __init__(self):\n",
|
||
" super(Net, self).__init__()\n",
|
||
" # 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution\n",
|
||
" # kernel\n",
|
||
" self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)\n",
|
||
" self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)\n",
|
||
" # an affine operation: y = Wx + b\n",
|
||
" self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)\n",
|
||
" self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)\n",
|
||
" self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" def forward(self, x):\n",
|
||
" # Max pooling over a (2, 2) window\n",
|
||
" x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))\n",
|
||
" # If the size is a square you can only specify a single number\n",
|
||
" x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)\n",
|
||
" x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))\n",
|
||
" x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))\n",
|
||
" x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))\n",
|
||
" x = self.fc3(x)\n",
|
||
" return x\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" def num_flat_features(self, x):\n",
|
||
" size = x.size()[1:] # all dimensions except the batch dimension\n",
|
||
" num_features = 1\n",
|
||
" for s in size:\n",
|
||
" num_features *= s\n",
|
||
" return num_features\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"net = Net()\n",
|
||
"print(net)"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"在模型中必须要定义 ``forward`` 函数, ``backward``\n",
|
||
"函数 (用来计算梯度) 会被``autograd``自动创建.\n",
|
||
"可以在 ``forward`` 函数中使用任何针对 Tensor 的操作.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" ``net.parameters()``返回可被学习的参数(权重)列表和值\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [
|
||
{
|
||
"name": "stdout",
|
||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||
"text": [
|
||
"10\n",
|
||
"torch.Size([6, 1, 5, 5])\n"
|
||
]
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"params = list(net.parameters())\n",
|
||
"print(len(params))\n",
|
||
"print(params[0].size()) # conv1's .weight"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"测试随机输入 32x32\n",
|
||
"注:这个网络(LeNet)期望的输入大小是32*32.如果使用MNIST数据集来训练这个网络,请把图片大小重新调整到32*32.\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 5,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [
|
||
{
|
||
"name": "stdout",
|
||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||
"text": [
|
||
"tensor([[-0.0204, -0.0268, -0.0829, 0.1420, -0.0192, 0.1848, 0.0723, -0.0393,\n",
|
||
" -0.0275, 0.0867]], grad_fn=<ThAddmmBackward>)\n"
|
||
]
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32)\n",
|
||
"out = net(input)\n",
|
||
"print(out)"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"将所有参数的梯度缓存清零,然后进行随机梯度的的反向传播:\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 6,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"net.zero_grad()\n",
|
||
"out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10))"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"<div class=\"alert alert-info\"><h4>Note</h4><p>``torch.nn`` 只支持小批量输入.整个 ``torch.nn``\n",
|
||
"包都只支持小批量样本,而不支持单个样本\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" 例如, ``nn.Conv2d`` 接受一个4维的张量\n",
|
||
" ``每一维分别是sSamples * nChannels * Height * Width(样本数*通道数*高*宽).``.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" 如果你有单个样本,只需使用 ``input.unsqueeze(0)`` 来添加其它的维数</p></div>\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"在继续之前,我们回顾一下到目前为止用到的类.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"**回顾:**\n",
|
||
" - ``torch.Tensor`` - 一个用过自动调用 ``backward()``实现支持自动梯度计算的*多维数组* \n",
|
||
" . 并且 保存关于这个向量的*梯度* w.r.t.\n",
|
||
" - ``nn.Module`` - 神经网络模块.封装参数,移动到GPU上运行,导出,加载等.\n",
|
||
" - ``nn.Parameter`` - 一种变量,当把它赋值给一个``Module``时,被*自动*的注册为一个参数.\n",
|
||
" - ``autograd.Function`` - 实现一个自动求导操作的前向和反向定义,每个变量操作至少创建一个函数节点,每一个``Tensor``的操作都回创建一个接到创建``Tensor``和*编码其历史*的函数的``Function``节点.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"**重点如下:**\n",
|
||
" - 定义一个网络\n",
|
||
" - 处理输入,调用backword\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"**还剩:**\n",
|
||
" - 计算损失\n",
|
||
" - 更新网络权重\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"损失函数\n",
|
||
"-------------\n",
|
||
"一个损失函数接受一对(output, target)作为输入,计算一个值来估计网络的输出和目标值相差多少.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"***译者注:output为网络的输出,target为实际值***\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"nn包中有很多不同的损失函数\n",
|
||
"` <https://pytorch.org/docs/nn.html#loss-functions>`_ .\n",
|
||
": ``nn.MSELoss``是一个比较简单的,他计算输出和目标的**均方误差**\n",
|
||
"例如:\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 7,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [
|
||
{
|
||
"name": "stdout",
|
||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||
"text": [
|
||
"tensor(1.3172, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)\n"
|
||
]
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"output = net(input)\n",
|
||
"target = torch.randn(10) # 随机值作为样例\n",
|
||
"target = target.view(1, -1) # 使target和output的shape相同\n",
|
||
"criterion = nn.MSELoss()\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"loss = criterion(output, target)\n",
|
||
"print(loss)"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"Now, if you follow ``loss`` in the backward direction, using its\n",
|
||
"``.grad_fn`` attribute, you will see a graph of computations that looks\n",
|
||
"like this:\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"::\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" input -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d\n",
|
||
" -> view -> linear -> relu -> linear -> relu -> linear\n",
|
||
" -> MSELoss\n",
|
||
" -> loss\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"So, when we call ``loss.backward()``, the whole graph is differentiated\n",
|
||
"w.r.t. the loss, and all Tensors in the graph that has ``requires_grad=True``\n",
|
||
"will have their ``.grad`` Tensor accumulated with the gradient.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"For illustration, let us follow a few steps backward:\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": null,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"print(loss.grad_fn) # MSELoss\n",
|
||
"print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0]) # Linear\n",
|
||
"print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0].next_functions[0][0]) # ReLU"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"反向传播\n",
|
||
"--------\n",
|
||
"调用loss.backward()获得反向传播的误差.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"但是在调用前需要清除已存在的梯度,否则梯度将被累加到已存在的梯度.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"现在,我们将调用loss.backward(),并查看conv1层的偏差(bias)项在反向传播前后的梯度.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [
|
||
{
|
||
"name": "stdout",
|
||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||
"text": [
|
||
"conv1.bias.grad before backward\n",
|
||
"tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])\n",
|
||
"conv1.bias.grad after backward\n",
|
||
"tensor([ 0.0074, -0.0249, -0.0107, 0.0326, -0.0017, -0.0059])\n"
|
||
]
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"net.zero_grad() # 清楚梯度\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"print('conv1.bias.grad before backward')\n",
|
||
"print(net.conv1.bias.grad)\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"loss.backward()\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')\n",
|
||
"print(net.conv1.bias.grad)"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"如何使用损失函数\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"**稍后阅读:**\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" `nn`包,包含了各种用来构成深度神经网络构建块的模块和损失函数,完整的文档请查看 `here <https://pytorch.org/docs/nn>`_.\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"**剩下的最后一件事:**\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" - 新网络的权重\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"更新权重\n",
|
||
"------------------\n",
|
||
"在实践中最简单的权重更新规则是随机梯度下降 (SGD):\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" ``weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient``\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"我们可以使用简单的Python代码实现这个规则:\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"```python\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
" learning_rate = 0.01\n",
|
||
" for f in net.parameters():\n",
|
||
" f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate)\n",
|
||
"```\n",
|
||
"但是当使用神经网络是,想要使用各种不同的更新规则,比如SGD,Nesterov-SGD,Adam, RMSPROP等.在PyTorch中构建了一个包``torch.optim``实现了所有的这些规则.\n",
|
||
"使用他们非常简单\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [],
|
||
"source": [
|
||
"import torch.optim as optim\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"# create your optimizer\n",
|
||
"optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)\n",
|
||
"\n",
|
||
"# in your training loop:\n",
|
||
"optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers\n",
|
||
"output = net(input)\n",
|
||
"loss = criterion(output, target)\n",
|
||
"loss.backward()\n",
|
||
"optimizer.step() # Does the update"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"source": [
|
||
".. Note::\n",
|
||
" \n",
|
||
" Observe how gradient buffers had to be manually set to zero using\n",
|
||
" ``optimizer.zero_grad()``. This is because gradients are accumulated\n",
|
||
" as explained in `Backprop`_ section.\n",
|
||
"\n"
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||
"execution_count": null,
|
||
"metadata": {},
|
||
"outputs": [],
|
||
"source": []
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"metadata": {
|
||
"kernelspec": {
|
||
"display_name": "Pytorch for Deeplearning",
|
||
"language": "python",
|
||
"name": "pytorch"
|
||
},
|
||
"language_info": {
|
||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||
"name": "ipython",
|
||
"version": 3
|
||
},
|
||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||
"name": "python",
|
||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
||
}
|
||
},
|
||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||
"nbformat_minor": 1
|
||
}
|